ALBA
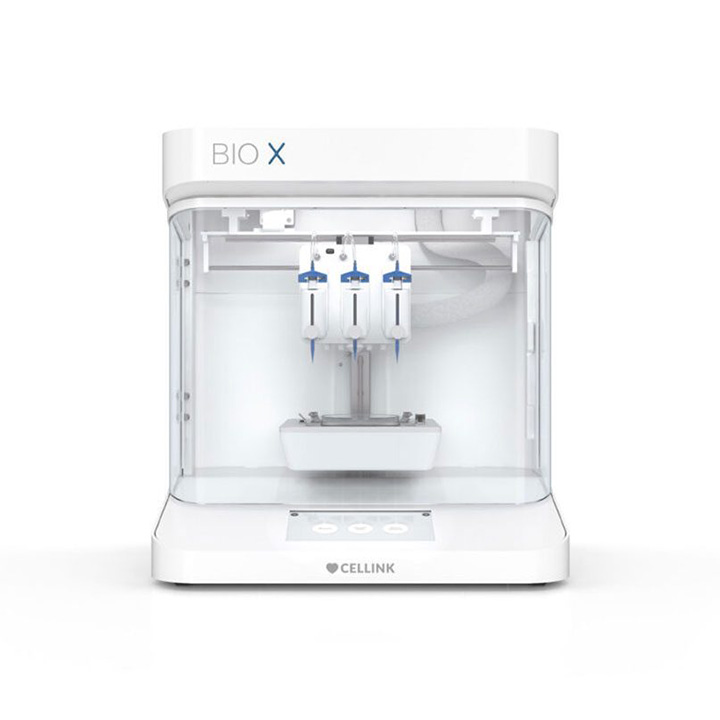
We are proud to present ALBA - Advanced Laboratory Bioprinting Applications, our next-generation bioprinter designed to revolutionize the field of biomedical research.
3D bioprinting ranges from new tissue regeneration methodologies to innovative solutions for diagnostic, monitoring, and personalized therapy technologies. For these reasons, it is not always possible to achieve advancements with standard bioprinters: there can be various approaches, strategies, and technological processes for the same application.
Given this need, we developed ALBA, a flexible and cutting-edge Made in Italy platform equipped with specially designed and customizable extrusion systems to meet the specific needs of every research activity.
It has been conceived to facilitate the experimentation of applications ranging from biosensors to therapy delivery devices, from personalized tissue avatars to regenerative medicine systems.
With ALBA, we welcome researchers’ requests and offer them a unique solution that supports experimentation and innovation, empowering them to explore new frontiers in personalized medicine with an advanced and customized tool tailored to the needs of each research project.
Bioprinting applications
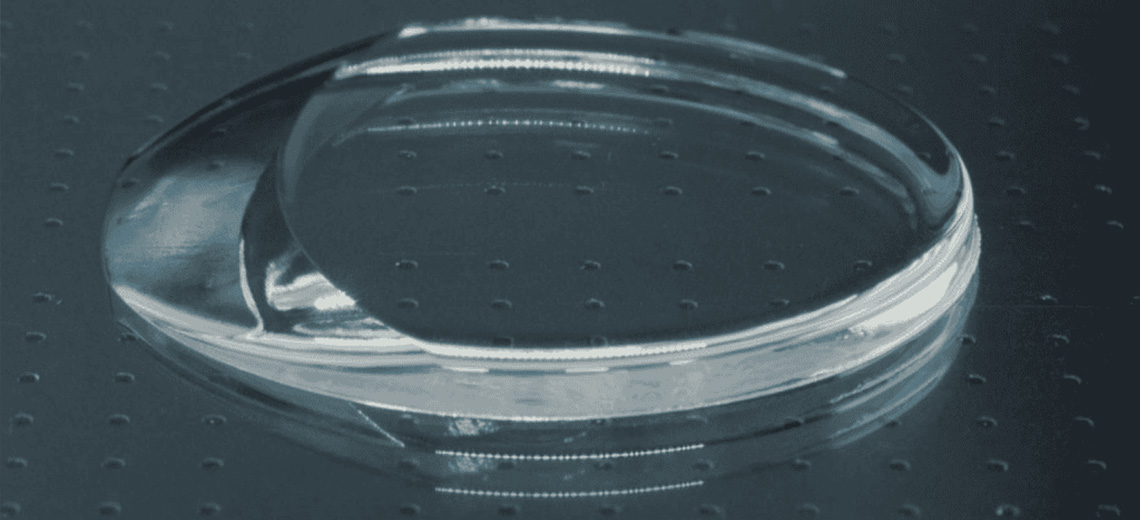

3D PRINTED ARTIFICIAL CORNEA
- corneal mimetic biopolymers and exosomes derived from stromal stem cells
- bioink layered on a support, stabilized through photo-crosslinking
- avascular and transparent tissues
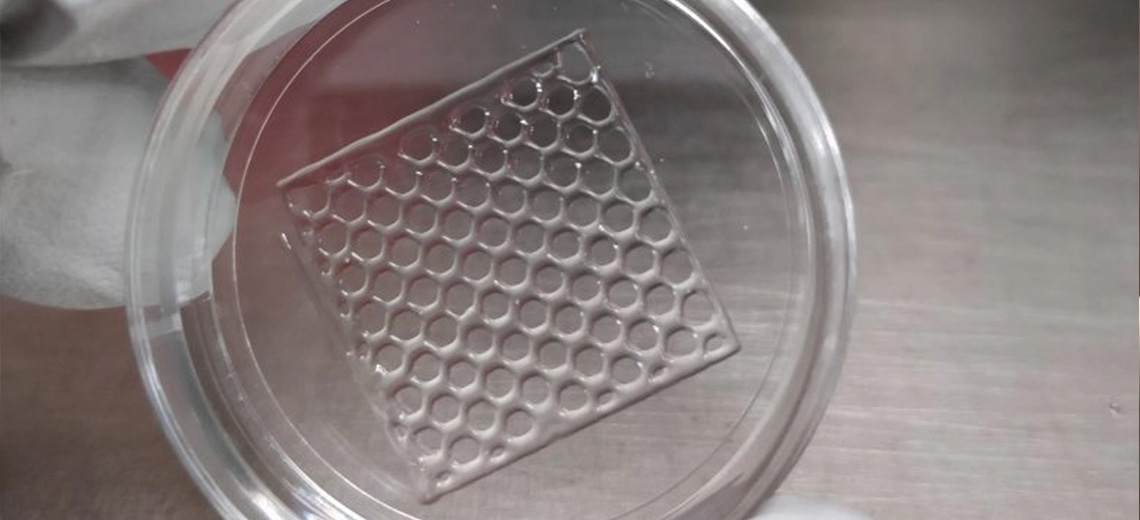
BIOSENSORS FOR GLUCOSE MEASUREMENT
- PVA UV hydrogel with dextran and conA labeled with fluorescent dyes, encapsulated in alginate microspheres
- printing on Petri dishes, cross-linking with UV light
- glucose detection in cell cultures, results comparable to commercial sensors
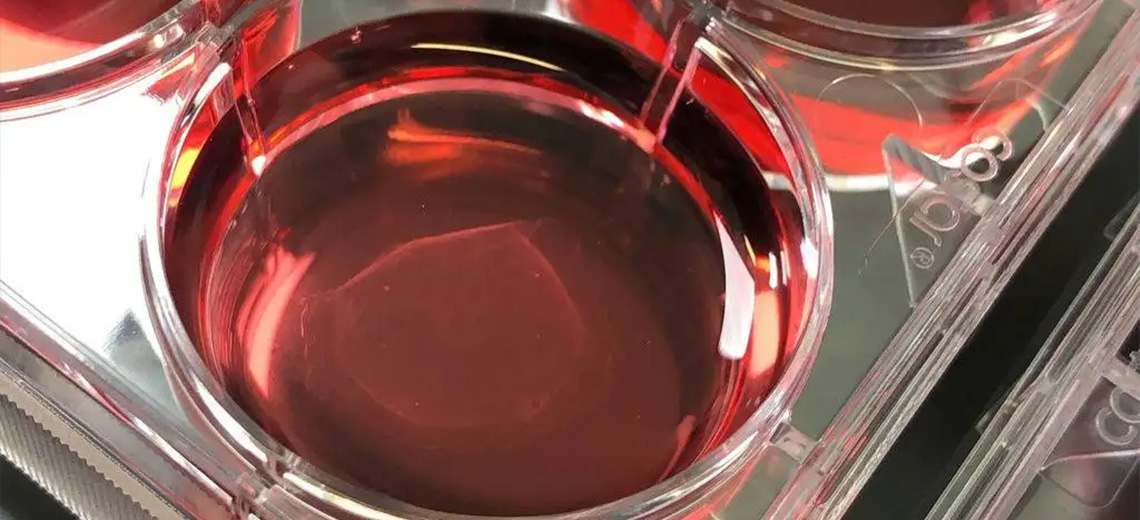

SKIN MODEL WITH HAIR FOLLICLES
- - bioink with human dermal cells and bioink with dermal papilla cells, endothelial cells, keratinocytes, and epidermal melanocytes
- collagen IV junction
- cell viability over 94%, structures similar to hair follicles